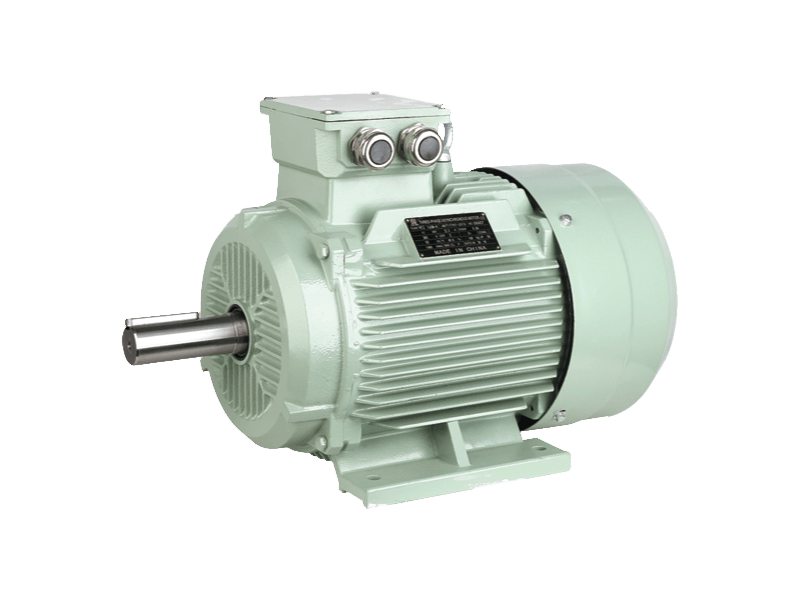
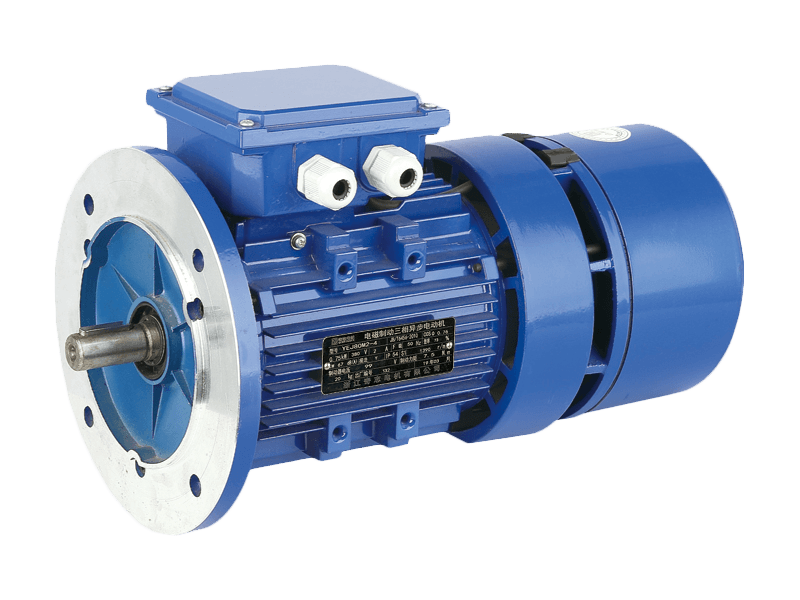
An
electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. This is done by a force between two opposing magnetic fields that are created by an electromagnet and produced by electrical currents.
An electromagnet is a magnet that has a north and south pole. The north end of a magnet will attract the south end of another magnet, and the south end of the magnet will repel the north.

Inside an electric motor, this attracting and repelling force produces rotational motion. A simple electromagnet is a bar magnet with its ends marked “north” and “south.”
The rotor of an electric motor has wire windings wrapped around a ferromagnetic core. The current flowing through these wires causes the field of the field magnet to turn the rotor.
They can be categorized by power supply, application, construction and type of movement output.
Constant speed motors are suited for frequent start-and-stop operations and for applications that require synchronous rotor speeds independent of load torque. These are commonly used in industrial automation and equipment such as pumps, fans and compressors.
The electric motor is the most widely used generator of electrical energy and accounts for more than a quarter of global electricity consumption. While they're a critical part of the energy grid, electric motors are not as advanced as they could be.