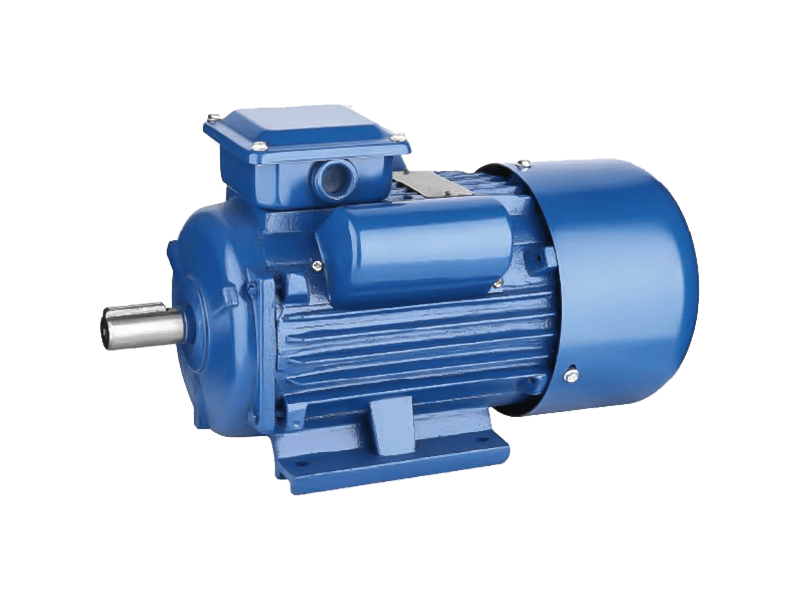
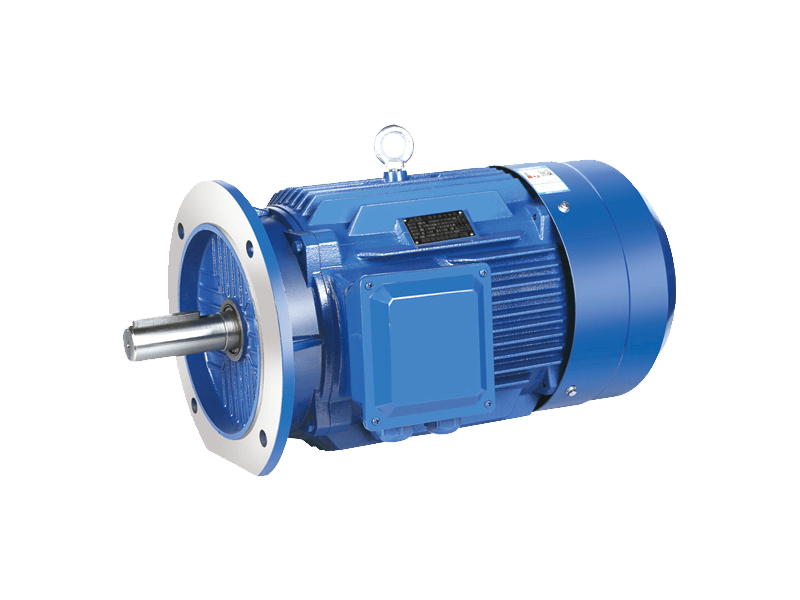
Three-phase asynchronous motors have long been the backbone of industrial machinery, powering a wide range of applications from factory assembly lines to HVAC systems. These robust and versatile machines are highly regarded for their efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice in industries worldwide. In this article, we will explore the key factors driving the increasing demand for three-phase asynchronous motors, their benefits, and the future trends shaping their continued growth in various industrial sectors.
Understanding Three-Phase Asynchronous Motors
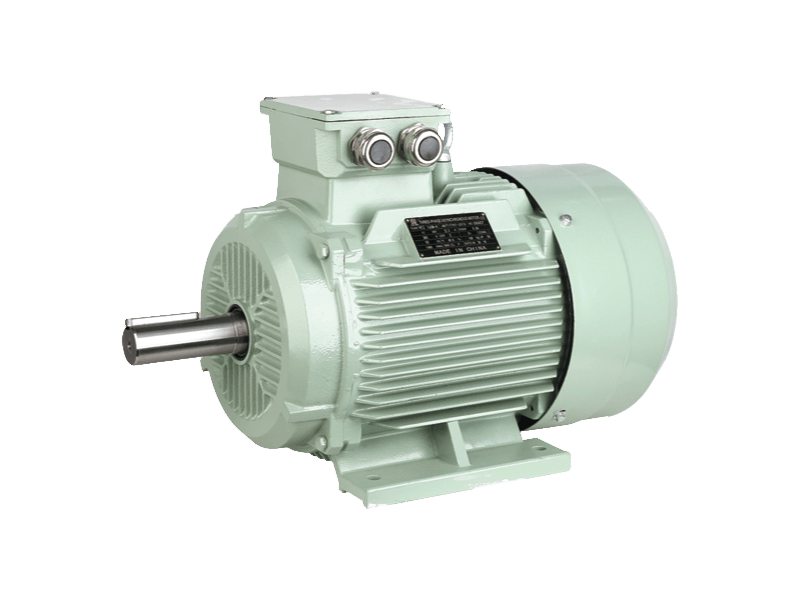
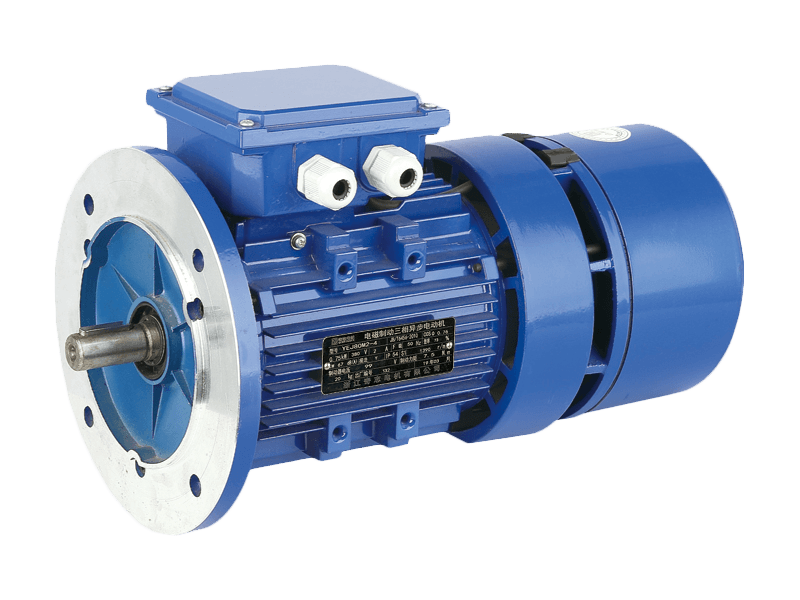
A three-phase asynchronous motor, also known as an induction motor, operates on a three-phase electric power supply, utilizing the principles of electromagnetic induction to convert electrical energy into mechanical power. The rotor in these motors does not rotate at the synchronous speed of the stator's magnetic field but instead lags behind it, which is where the term "asynchronous" comes from. This feature allows them to operate efficiently across various loads without the need for complex control systems, making them ideal for continuous operation in industrial settings.
Key Benefits of Three-Phase Asynchronous Motors
1. High Efficiency and Reliability
One of the main reasons for the growing adoption of three-phase asynchronous motors is their exceptional energy efficiency. These motors deliver higher efficiency compared to their single-phase counterparts, reducing energy consumption and operational costs. The three-phase power supply ensures that the motor runs smoothly and consistently, even under variable load conditions. This reliability is especially important in industries where downtime can result in costly delays and disruptions.
In addition to energy efficiency, three-phase asynchronous motors are renowned for their long service life. Their simple construction and robust design make them resistant to wear and tear, allowing them to perform consistently over extended periods. This durability is a key factor in their widespread use across a variety of industrial applications, including pumps, compressors, conveyor belts, and mixers.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial cost of three-phase asynchronous motors may be higher than that of single-phase motors, they offer significant long-term savings due to their lower energy consumption and minimal maintenance requirements. These motors are often designed to withstand harsh operating conditions, meaning that they require less frequent repairs or replacements, resulting in reduced lifecycle costs.
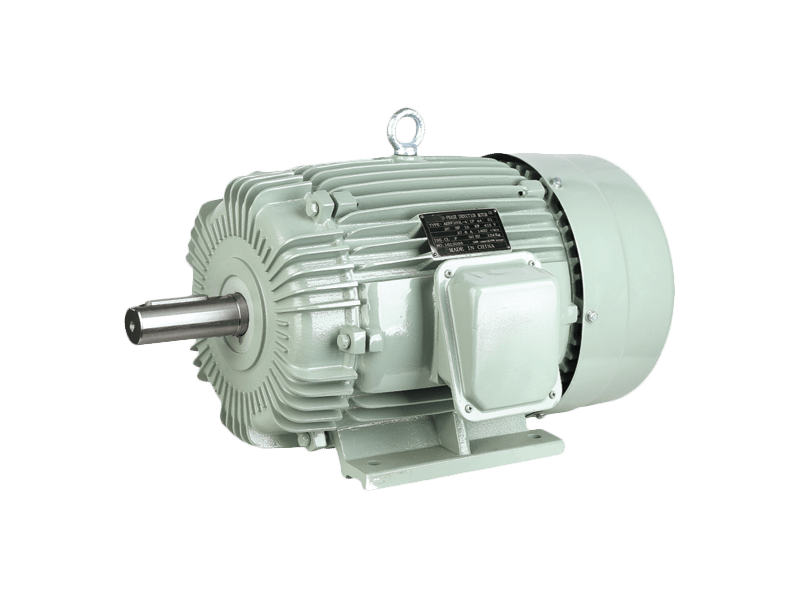
Moreover, the relatively low maintenance needs of three-phase asynchronous motors contribute to their cost-effectiveness. The lack of brushes or commutators in the motor’s design eliminates many of the components that typically require maintenance in other motor types, further reducing costs for industrial operations.
3. Versatility and Scalability
Three-phase asynchronous motors are incredibly versatile and can be used in a wide range of industrial applications, from small machines to large-scale manufacturing plants. Their scalability makes them suitable for everything from simple home appliances to complex industrial systems. These motors can be easily adapted to meet specific performance needs, whether it’s controlling the speed, torque, or power output.
Furthermore, three-phase asynchronous motors can be equipped with variable frequency drives (VFDs) to adjust their speed and performance characteristics. This flexibility is highly beneficial in industries where varying operational speeds are required, such as in conveyors, elevators, and escalators.
4. Environmental Impact
As industries increasingly turn their focus to sustainability, three-phase asynchronous motors are emerging as a solution for reducing the carbon footprint of industrial operations. These motors, when paired with advanced energy-efficient technologies, can significantly reduce energy consumption, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the widespread use of three-phase asynchronous motors in large industrial operations can lead to considerable savings in overall energy consumption, reducing the demand on electrical grids and helping to address global energy challenges.